
13
November 2020
301 vs. 302 Redirects & SEO: The What, Why & How
301 vs. 302 redirects. Confused about which one to use?
You’re not the only one.
Even in 2019, website owners are unclear about which type of redirect is best for SEO.
At its simplest, “a redirect is a way to send both users and search engines to a different URL from the one they originally requested.”
You might want to redirect a page for a variety of reasons, including:
- The URL is broken.
- You have a new website or page.
- You’re fixing a webpage and want users to go to a different page while the old one is under construction.
The purpose of the redirect certainly impacts which one you should choose. It’s important to know the difference between the two because choosing the wrong option could impact your SEO efforts.
Choosing the correct redirect guarantees that you’ll at least maintain your current rankings as well as continue to solidify the positive reputation you’ve built for your brand through backlinks and content creation.
So the question is: which redirect is best for SEO?
What Is a 301 Redirect?
A 301 redirect sends the message to search engines that a website or page has been moved permanently.
Permanent means around a year or longer. After a year, check to see if people are still being redirected to your site.
If they are, figure out where they’re coming from and try to fix the source before you cancel the redirect.
Check out this article by Search Engine Journal to learn more about when it’s safe to kill redirects.
When Should You Use 301 Redirects?
Many people use this type of redirect when they purchase domains that they want being sent to their primary domain (misspellings of a brand, variations of your brand, or relevant domains with high “Domain Authority”).
It’s also helpful to use a 301 when establishing which domain is your default site: “www.yourwebsite.com” or just “yourwebsite.com”.
People tend to leave out the “www” when writing or typing out website names, so a permanent redirect will guarantee they end up on your site even if they forget to type “www”.
It’s also appropriate to use a 301 if you’ve merged two websites together or have outdated URLs for any other reason.
What Is a 302 Redirect?
A 302 redirect lets search engines know that a website or page has been moved temporarily.
When Should You Use 302 Redirects?
You would use this type of redirect if you want to send users to a new site or page for a short period of time, such as when you’re redesigning or updating your website.
You only use a 302 if you’re planning on eventually bringing the old page back. You could also use a 302 redirect if you want to test out a new page and get some consumer feedback without hurting your rankings from the original page.
How Do Both Redirects Impact SEO?
When you use a 301, Google removes the old page from their index and most value (link equity) from that page is transferred to the new one.
That being said, it’s important to note that anytime you move a page from one URL to another, it will take search engines some time to notice the change and see any potential impact/change in rankings.
When used correctly, a 302 redirect will not hurt your SEO efforts.
When you choose this type of redirect, the original page remains indexed in Google and no value (link equity) is transferred to the new URL because Google knows this is just temporary. Thus you’ll retain any rankings, traffic value, and authority that page might have.
Where problems tend to rise is when people don’t know the difference between the two and they choose a 302 to redirect a site permanently.
Basically, what they’re doing is creating a new website or page and not transferring over any of the value they’ve accrued over time.
Hence why it’s important to understand the difference between a 301 and a 302, and when it’s appropriate to use both.

How to Implement Redirects
According to Google, in order “to implement a 301 redirect for websites that are hosted on servers running Apache, you’ll need access to your server’s .htaccess file.”
If you’re not sure how to do this, they offer an Apache Tutorial and a URL Rewriting Guide. If your server doesn’t run on Apache you’ll have to contact your host for direction.
If your site uses WordPress, you can take advantage of the following plugins that are intended to make redirection as easy as possible.
Some helpful plugins are:
- Redirection: This is intended for 301 redirects and 404 errors.
- Simple 301 Redirects: This only works on 301 redirects, but it works well.
- SEO Redirection: This plugin helps users create both 301 and 302 redirects.
A Side Note on 404s
It’s important to at least briefly mention the 404 code in an article on redirects as this is also a common error that can impact SEO.
A 404 isn’t actually a redirect, though – it’s an error code meaning “not found”.
404 errors occur when a webpage is deleted from a site and a server, but links to the page still remain.
When a user types in or clicks on the link, they’re directed to a 404 “Page Not Found” error message. This can potentially have a negative impact on your SEO performance since it doesn’t provide an ideal user experience.
It’s frustrating to your customers to end up on a dead page. This is where the use of 301 and 302 redirects come into play, as they can solve the “page not found” errors from occurring.
To find 404 errors, simply log into Google Search Console and navigate to the “coverage” section as shown below.
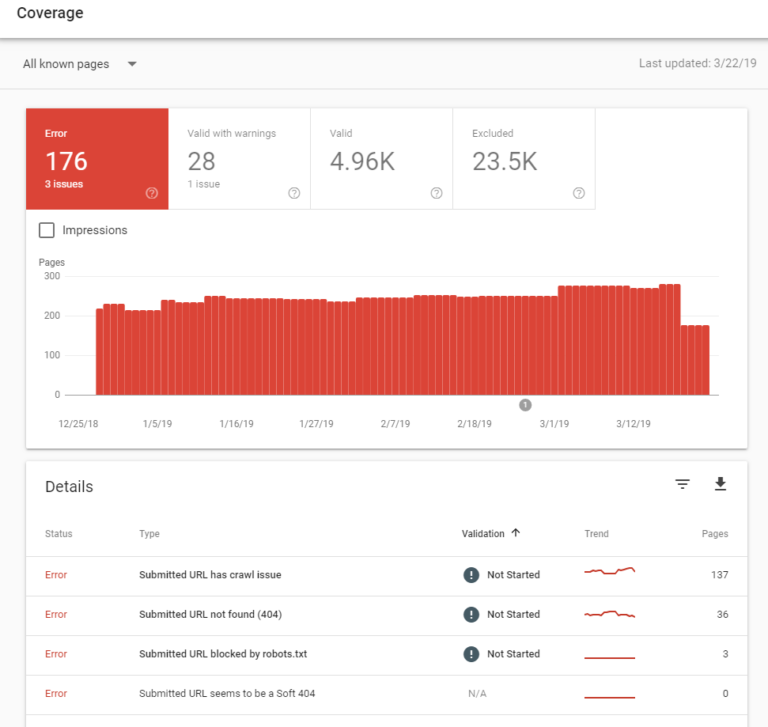
This will allow you to click on the 404 section and identify all the URLs resulting in these errors. It would be recommended to check this report regularly and set up the proper redirects where applicable.
The Takeaway
Use whatever type of redirect is best for your intended purpose and goals.
Educate yourself on the differences, and make sure you’re using the correct redirect for the correct outcome.
If you use a 302 with the expectation that the change will be temporary, and you find later on that it becomes a permanent change, be sure to change the redirect from a 302 to a 301.
Finally, monitor your rankings to ensure that Google is able to index your new pages and that you haven’t made an error which will cause your rankings to suffer.
Source: www.searchenginejournal.com

